Treatment Overview
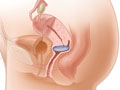
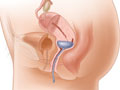
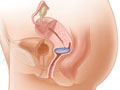
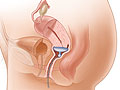
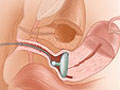
A vaginal pessary is a removable device placed into the vagina. It is designed to support areas of pelvic organ prolapse.
A variety of pessaries are available, including the ring, inflatable, doughnut, and Gellhorn.
Your doctor will fit your pessary to hold the pelvic organs in position without causing discomfort. Pessaries come in different sizes and should be fitted carefully.
Pessaries can be used successfully to treat other gynecologic conditions, such as a uterus that is in the wrong position or stress incontinence.
What To Expect
Your pessary will be fitted at your doctor's office. You may need to experiment with different kinds of pessaries to find one that feels right for you. Your doctor will teach you how to remove, clean, and reinsert the pessary on a regular schedule. If it's hard for you to remove and replace your pessary, you can have it done regularly at your doctor's office.
Depending on your comfort level and the type of pessary, you may be able to leave the pessary in during vaginal sex. But you can't insert a diaphragm (a round rubber device used as a barrier method of birth control) while wearing a pessary. If you have not reached menopause, you may want to discuss birth control with your doctor.
Why It Is Used
Pessaries are used as a nonsurgical approach to the treatment of pelvic organ prolapse.
Pessaries are also used when symptoms of pelvic organ prolapse are mild or when childbearing is not complete. They can be used in people who have other serious chronic health problems, such as heart or lung disease, that make a surgical procedure more dangerous.
Pessaries are sometimes used to see what the effect of surgery for pelvic organ prolapse will be on urinary symptoms. This is called a "pessary test." If you have a problem with incontinence with a pessary inserted, a separate surgery to fix the incontinence problem may be done at the same time as a prolapse surgery.
Pessaries are sometimes used to treat uterine prolapse during pregnancy. In this instance, the pessary holds the uterus in the correct position before it enlarges and becomes trapped in the vaginal canal.
Pessaries are also used to help treat stress incontinence.
How Well It Works
Pessaries do not cure pelvic organ prolapse but help with symptoms and slow the progression of prolapse. They add support to the vagina and increase tightness of the tissues and muscles of the pelvis. Symptoms improve for many people who use a pessary. And for some, symptoms go away.
Risks
Possible complications from wearing a pessary include:
- Open sores in the vaginal wall.
- Increase in vaginal discharge or odor.
- Bleeding.
- Wearing away of the vaginal wall. In severe cases, an opening (fistula) can form between the vagina and the rectum.
- Bulging of the rectum against the vaginal wall (rectocele formation).
Complications can be minimized by having a pessary that fits correctly and that does not put too much pressure on the wall of the vagina. Your pessary should be checked frequently by your doctor until both of you are satisfied with the fit.
After menopause, estrogen (cream, ring, or tablets) is sometimes used with a pessary to help with irritation caused by the pessary.
Follow your doctor's instructions for cleaning your pessary. Regular cleaning reduces the risk of complications. The cleaning schedule is determined by the type of pelvic organ prolapse and the specific brand of pessary.
Credits
Current as of: April 30, 2024